
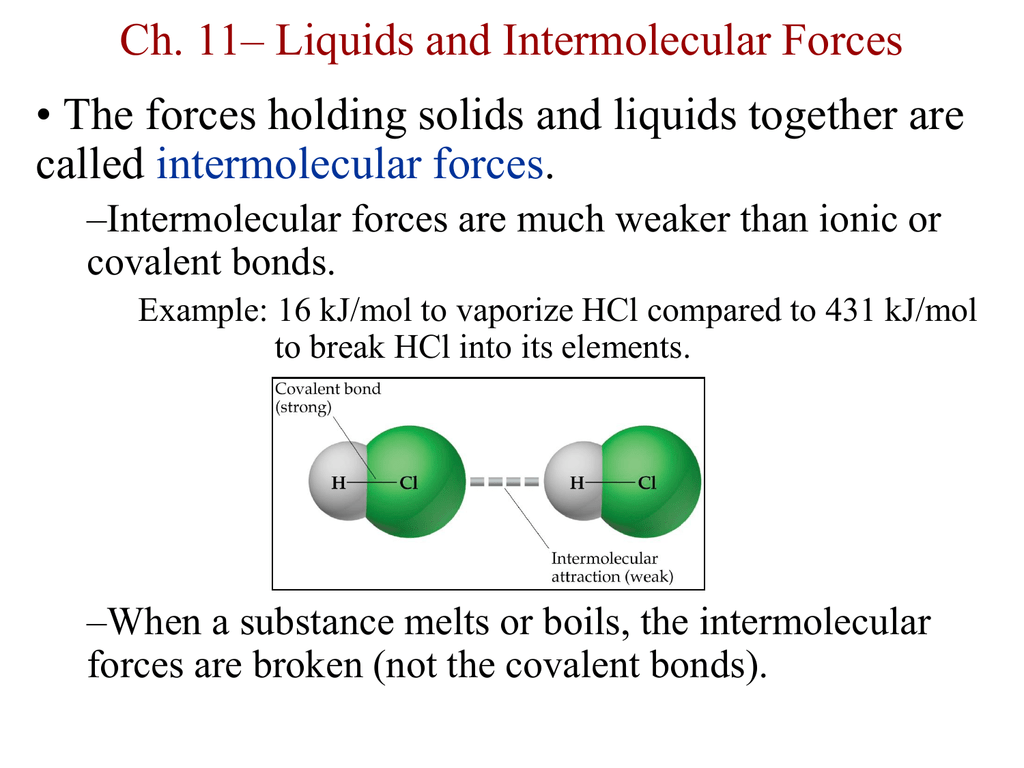
Intermolecular forces give rise to a number of structural features and properties of liquids.What types of intermolecular forces are present in:.Would you expect to find hydrogen bonds in:.Diatomic chlorine and carbon tetrabromide c. What types of intermolecular forces exist between the following pairs: a.Cations are less polarizable than their parent atoms because they are smaller anions are more polarizable because they are larger.Polarizability decreases from left to right across a period because the increasing Zeff shrinks atomic size and holds the electrons more tightly.Polarizability increases down a group because atomic size increases, so the larger electron clouds are farther from the nucleus and, thus, easier to distort.Smaller atoms (or ions) are less polarizable than larger ones because their electrons are closer to the nucleus and therefore are held more tightly. The ease with which the electron cloud of a particle can be distorted is called its polarizability.*It is important to remember that the 3 intermolecular forces mentioned above are relatively weak in comparison to the covalent bond within a molecule.These types of bonds tend to not follow the relationship between MM and boiling points.Only between N-H, O-H, and F-H bonds have hydrogen bonding. This a special, strong type of dipole-dipole interaction between hydrogen and polar bond in elements nitrogen, oxygen, and fluorine.Polar molecules tend to have slightly higher boiling and melting points than non-polar substances of similar MM.The larger the dipole moment then the greater the dipole force.These are attractive forces between polar molecules.As molar mass (MM) increases the dispersion forces become stronger, consequently the boiling point of non-polar molecules tend to increase with MM.These forces can only occur in non-polar molecules.This happens when something (cation or polar compound) “throws off” the distribution of electrons in an atom or molecule.The attractive forces that arise as a result of temporary dipoles induced in atoms or molecules.The stronger the intermolecular force the higher the boiling or melting point. They tend to have low melting and boiling points.Generally, are insoluble in water but soluble in non-polar solvents.
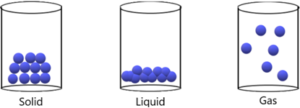
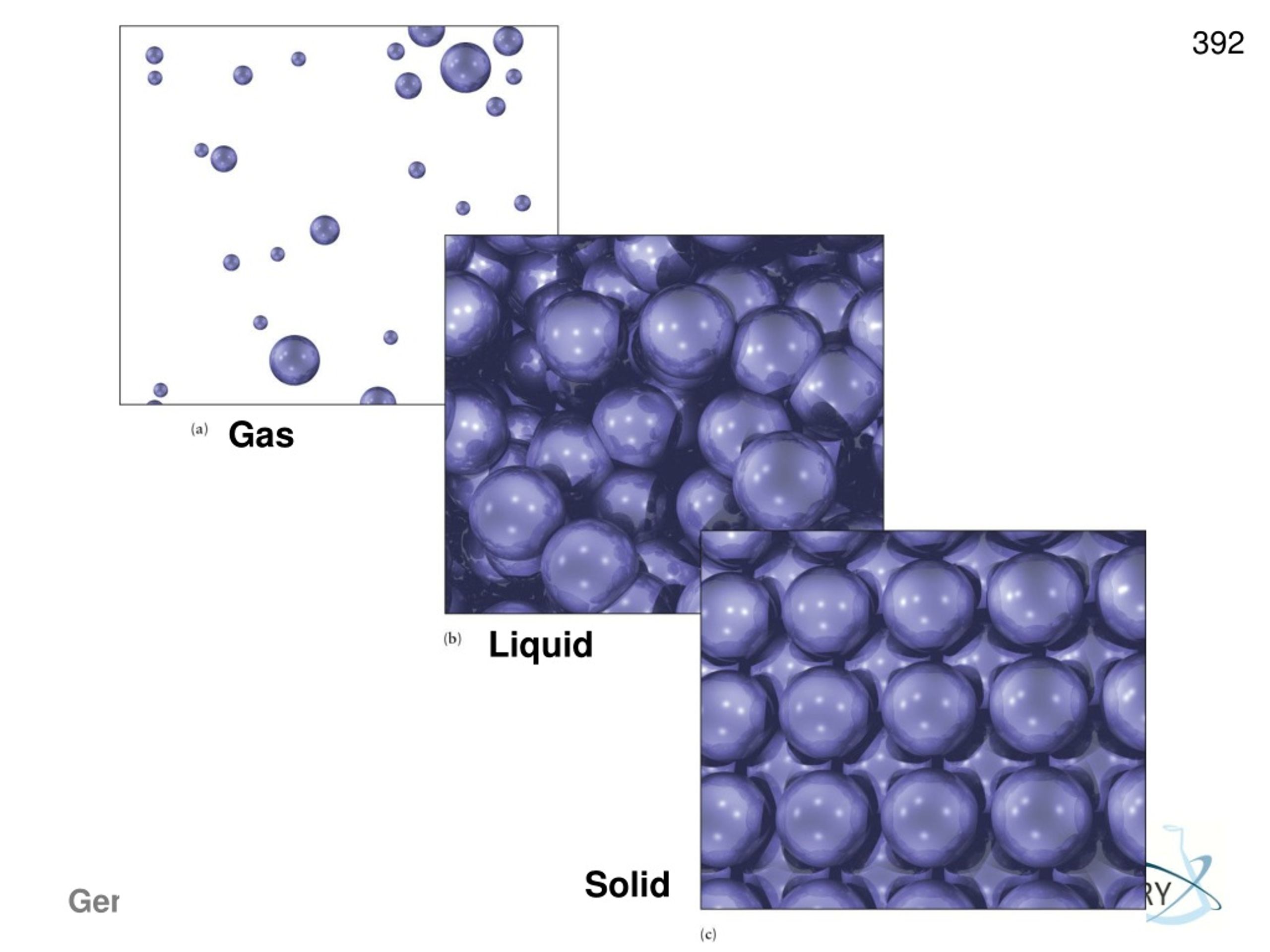
Molecular substances tend to have the following characteristics:.Boiling points and melting points often reflect the strength of these intermolecular forces.Keep in mind that intramolecular forces are forces within a molecule, and intermolecular forces are between molecules.And these forces are why liquids and solids do not present “ideal behavior”. These forces are partly responsible for the non-ideal gas law behavior discussed earlier.These are attractive forces between molecules:.So that they have a definite volume and shape. Solids – molecules are held rigidly in a position with virtually no freedom of motion.Allowing for a definite volume but taking the shape of it’s container. Liquids – the molecules are so close together that there is little empty space.Distance between gas molecules are so great at ordinary temperatures and pressures (25 *C and 1atm) that there is no real interaction between gas molecules.The Kinetic Molecular Theory of Liquids & Solids– Chapter 9


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
